Pattern Recognition 2022 Paper
Danilo Avola1, Luigi Cinque1, Alessio Fagioli1, Gian Luca Foresti2, Adriano Fragomeni3, Daniele Pannone1
1Sapienza University of Rome, 2University of Udine, 3University of Bristol
Abstract
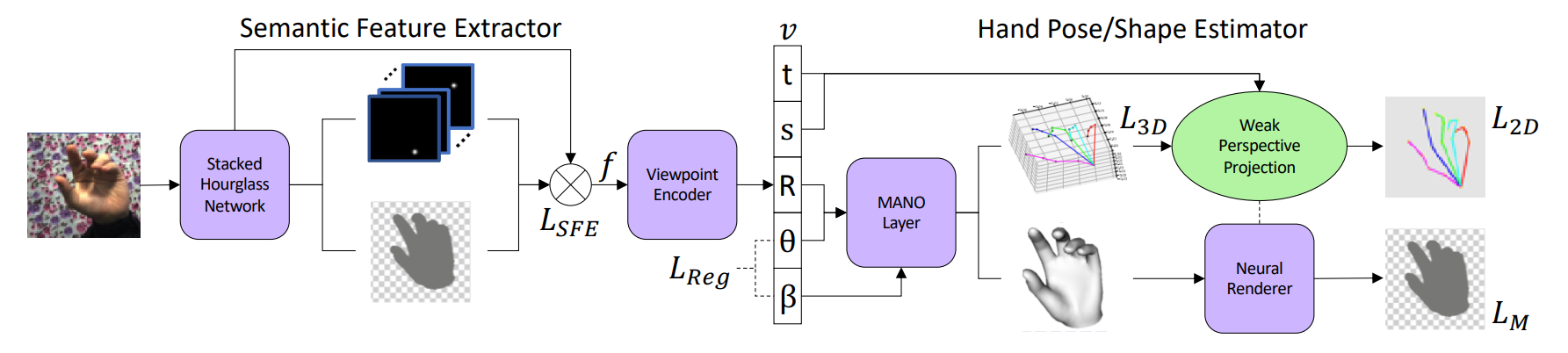
Estimating the 3D pose of a hand from a 2D image is a well-studied problem and a requirement for several real-life applications such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and hand gesture recognition. Currently, reasonable estimations can be computed from single RGB images, especially when a multi-task learning approach is used to force the system to consider the shape of the hand when its pose is determined. However, depending on the method used to represent the hand, the performance can drop considerably in real-life tasks, suggesting that stable descriptions are required to achieve satisfactory results. In this paper, we present a keypoint-based end-to-end framework for 3D hand and pose estimation and successfully apply it to the task of hand gesture recognition as a study case. Specifically, after a pre-processing step in which the images are normalized, the proposed pipeline uses a multi-task semantic feature extractor generating 2D heatmaps and hand silhouettes from RGB images, a viewpoint encoder to predict the hand and camera view parameters, a stable hand estimator to produce the 3D hand pose and shape, and a loss function to guide all of the components jointly during the learning phase. Tests were performed on a 3D pose and shape estimation benchmark dataset to assess the proposed framework, which obtained state-of-the-art performance. Our system was also evaluated on two hand-gesture recognition benchmark datasets and significantly outperformed other keypoint-based approaches, indicating that it is an effective solution that is able to generate stable 3D estimates for hand pose and shape.
Paper
Bibtex
@article{AVOLA2022108762,
title = {3D hand pose and shape estimation from RGB images for keypoint-based hand gesture recognition},
journal = {Pattern Recognition},
volume = {129},
pages = {108762},
year = {2022},
issn = {0031-3203},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108762},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320322002436},
author = {Danilo Avola and Luigi Cinque and Alessio Fagioli and Gian Luca Foresti and Adriano Fragomeni and Daniele Pannone},
keywords = {Hand pose estimation, Hand shape estimation, Deep learning, Hand gesture recognition},
abstract = {Estimating the 3D pose of a hand from a 2D image is a well-studied problem and a requirement for several real-life applications such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and hand gesture recognition. Currently, reasonable estimations can be computed from single RGB images, especially when a multi-task learning approach is used to force the system to consider the shape of the hand when its pose is determined. However, depending on the method used to represent the hand, the performance can drop considerably in real-life tasks, suggesting that stable descriptions are required to achieve satisfactory results. In this paper, we present a keypoint-based end-to-end framework for 3D hand and pose estimation and successfully apply it to the task of hand gesture recognition as a study case. Specifically, after a pre-processing step in which the images are normalized, the proposed pipeline uses a multi-task semantic feature extractor generating 2D heatmaps and hand silhouettes from RGB images, a viewpoint encoder to predict the hand and camera view parameters, a stable hand estimator to produce the 3D hand pose and shape, and a loss function to guide all of the components jointly during the learning phase. Tests were performed on a 3D pose and shape estimation benchmark dataset to assess the proposed framework, which obtained state-of-the-art performance. Our system was also evaluated on two hand-gesture recognition benchmark datasets and significantly outperformed other keypoint-based approaches, indicating that it is an effective solution that is able to generate stable 3D estimates for hand pose and shape.}
}
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by MIUR under grant “Departments of Excellence 2018-2022” of the Department of Computer Science of Sapienza University.